Experiencing fogging in your gas mask can be frustrating and even dangerous, especially in critical situations. Understanding how to keep US military gas masks from fogging is essential for clear visibility and safety.
To keep US military gas masks from fogging, regular maintenance, proper fitting, and the use of anti-fogging agents are crucial. Implementing ventilation techniques and choosing appropriate moisture-control clothing also play a significant role in maintaining clear vision through the mask.
From selecting the right anti-fogging products to mastering effective breathing techniques, each section below provides valuable insights tailored for preppers and the general public alike. Whether you’re facing extreme weather or demanding tactical scenarios, these guidelines will equip you with the knowledge to maintain optimal functionality of your gas mask.
Common Causes of Fogging in Military Gas Masks
Fogging in gas masks, particularly in military settings, can be a significant hindrance, compromising both visibility and safety. Understanding the various factors that contribute to this issue is crucial for effective prevention.
Breath
When a soldier exhales in a gas mask, the warm, moist air from their breath meets the cooler surface of the mask’s lens. This meeting of warm air and a cool surface results in condensation, leading to the formation of fog.
This phenomenon is similar to how a bathroom mirror fogs up during a hot shower. The condensation blurs the mask’s lens, significantly impairing the wearer’s vision. This not only affects operational efficiency but also can be a safety hazard in critical situations.
External and Internal Temperature Variations
The impact of temperature variations on gas mask fogging cannot be overstated. Soldiers operating in environments with fluctuating temperatures face a higher risk of their masks fogging up. For instance, moving from the cold outdoor air into a heated vehicle or building can cause the lenses of a gas mask to fog up rapidly. The disparity between the warm, humid air inside the mask and the cold, dry air outside creates an ideal environment for condensation.
To address this challenge, it’s important to consider both mask design and usage strategies. Masks with better insulation and thermal regulation can minimize the temperature differential between the inside and outside air.
Furthermore, soldiers can be trained in techniques to acclimate their masks when transitioning between different environments, such as briefly exposing the mask to outside air to equalize the temperature before fully entering a new environment. These approaches help in maintaining clear vision and operational readiness in varying temperature conditions.
Gas Mask Seal
The effectiveness of a gas mask in preventing fogging largely depends on its seal.
A well-sealed mask ensures that the warm, moist air exhaled by the wearer does not escape and condense on the cooler lens. An improper seal, on the other hand, allows this air to escape, leading to fogging.
Therefore, ensuring a proper seal is as crucial for visibility as it is for protection against contaminants.
Regular fit testing is essential to ensure the integrity of the gas mask seal. Soldiers should be trained to check their masks for any signs of wear and tear that might compromise the seal. Additionally, the design of the mask plays a vital role; masks with adjustable straps and components that can conform to different face shapes help in achieving a better seal. By prioritizing the maintenance of a proper seal, the risk of fogging can be significantly reduced, enhancing both the safety and effectiveness of military personnel.
Effects of Fogging on Military Operations

Fogging in gas masks poses a serious threat to military operations. It can drastically reduce a soldier’s situational awareness, obscuring their vision and making it difficult to read instruments or recognize signals and threats.
In high-stakes situations, such as in combat or hazardous environments, impaired vision can lead to critical errors, misjudgments, and potentially life-threatening situations.
Furthermore, the need to frequently clear fogged lenses can distract soldiers from their tasks, reducing operational efficiency and effectiveness. This issue also has psychological impacts; it can increase stress levels and reduce confidence in equipment, which in turn can affect performance.
Therefore, addressing the issue of fogging is not just a matter of convenience but a vital aspect of operational readiness and personnel safety. Effective training, proper equipment maintenance, and the use of anti-fogging technologies are essential components in ensuring that soldiers can perform their duties effectively and safely.
Now that we got those out of the way, how do you keep your military gas mask from fogging?
1. Ensuring Proper Gas Mask Fit
Achieving the perfect fit for a gas mask is not just about comfort; it’s a critical factor in ensuring the effectiveness and safety of the mask. As stated by Travis Robbins, Team Lead at the Protection Assessment Test System (PATS) laboratory:
“When you wear a gas mask, it seals around the skin. The whole point is a skin seal.”
A well-fitted mask provides an airtight seal, preventing harmful substances from entering while also reducing the risk of fogging.
In the following sections, we’ll delve into the key elements of achieving a perfect seal, a step-by-step guide for adjusting the mask, and troubleshooting common fit issues.
Key Elements for a Perfect Gas Mask Seal
Achieving a perfect seal in a gas mask is critical for effective protection against hazardous environments and for preventing the inconvenience and danger of fogging. The three main elements in ensuring this perfect seal are the facepiece material, strap tension, and the mask’s size and shape.
- Facepiece Material: The facepiece is the part of the mask that comes in direct contact with the skin. It’s essential that this material is flexible enough to conform closely to the contours of the face, ensuring no gaps through which contaminants can enter. However, flexibility shouldn’t compromise the material’s durability. The facepiece must be sturdy enough to withstand various environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and chemical exposure, without degrading. Additionally, the material should be hypoallergenic to avoid skin irritation, especially during prolonged use.
- Strap Tension: The tension of the mask’s straps plays a crucial role in maintaining a secure fit. Straps should be adjustable to accommodate different head sizes and shapes. They need to be tightened to a point where the mask feels snug against the face, but not so tight that it causes discomfort, which could lead to distraction or the need to frequently adjust the mask. Equally, straps that are too loose will not hold the mask securely, leading to potential leaks and fogging due to poor sealing.
- Proper Size and Shape: Gas masks are not one-size-fits-all. They come in various sizes and shapes to cater to different facial structures. Selecting a mask that closely matches the size and shape of your face is vital for creating an effective seal. A mask that’s too small will not cover all necessary areas, while one that’s too large may leave gaps. Additionally, the shape of the mask should complement the contours of the face, particularly around critical areas such as the nose bridge and chin.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adjusting Your Gas Mask Fit
Properly adjusting a gas mask is a critical step in ensuring both safety and comfort. Here’s a detailed guide on how to achieve the right fit:
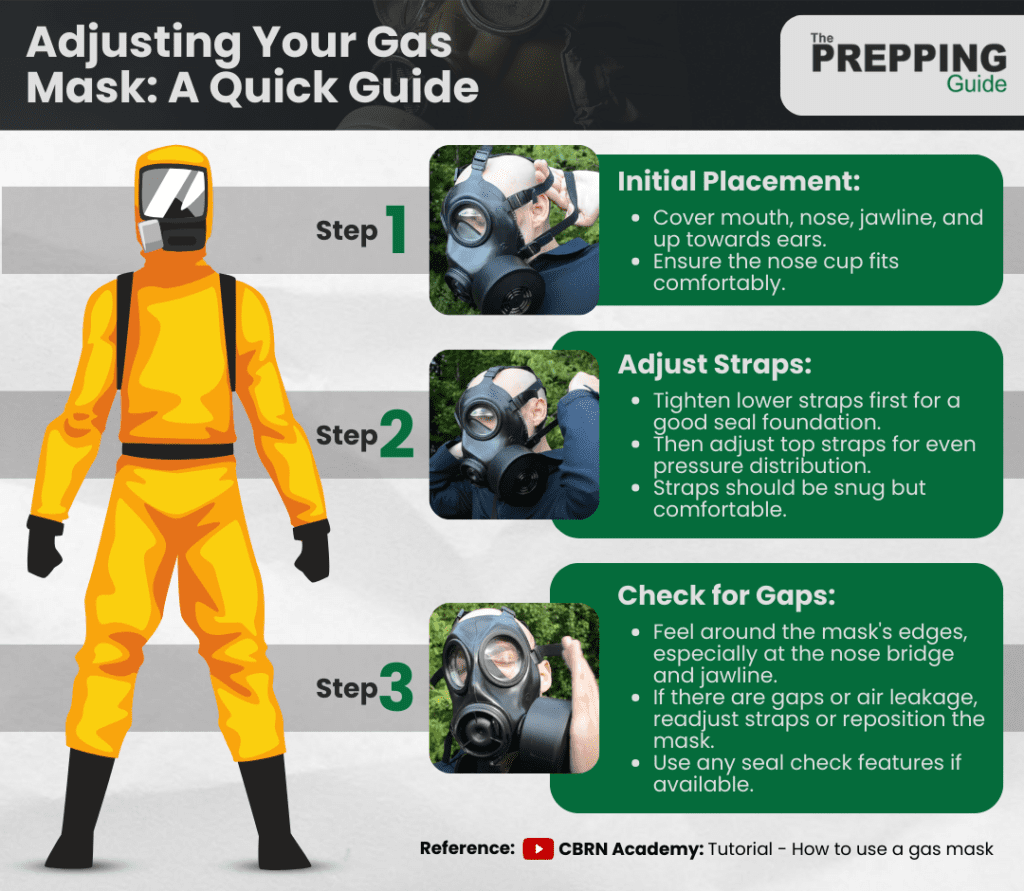
And here’s a video to help you understand the process better:
Troubleshooting Common Fit Issues with Military Gas Masks
Even with careful adjustment, some common issues can arise, affecting the mask’s fit and function. Here’s how to troubleshoot these issues:
- Air Leaks: If you detect air leaks, it often indicates that the mask is either not properly centered on your face or the straps are not correctly adjusted. Re-center the mask, ensuring it sits evenly on your face, and readjust the straps. For a quick check, you can perform a negative pressure test by covering the filters and inhaling gently. If the mask collapses slightly on your face without any air leaks, the seal is good.
- Discomfort: Discomfort can arise if the mask is too tight, causing pressure points, or too loose, leading to chafing. Adjust the straps to distribute pressure evenly. If discomfort persists, it might be due to the wrong mask size or shape. In this case, trying a different size or model may be necessary.
- Persistent Fogging: If fogging continues despite a proper fit, it might be due to high humidity inside the mask or temperature differences between the inside and outside of the mask. Check the mask’s internal structure for any issues that might impede airflow, like blocked or malfunctioning valves. Using anti-fogging solutions or wipes can also help. In some cases, installing a microfan or using anti-fog inserts might be necessary for persistent fogging issues.
2. Using Anti-Fogging Agents and Solutions
In addition to ensuring a proper mask fit, another effective approach to combat lens fogging in military gas masks is the use of anti-fogging agents and solutions. These can range from specially designed commercial products to simple, homemade remedies.
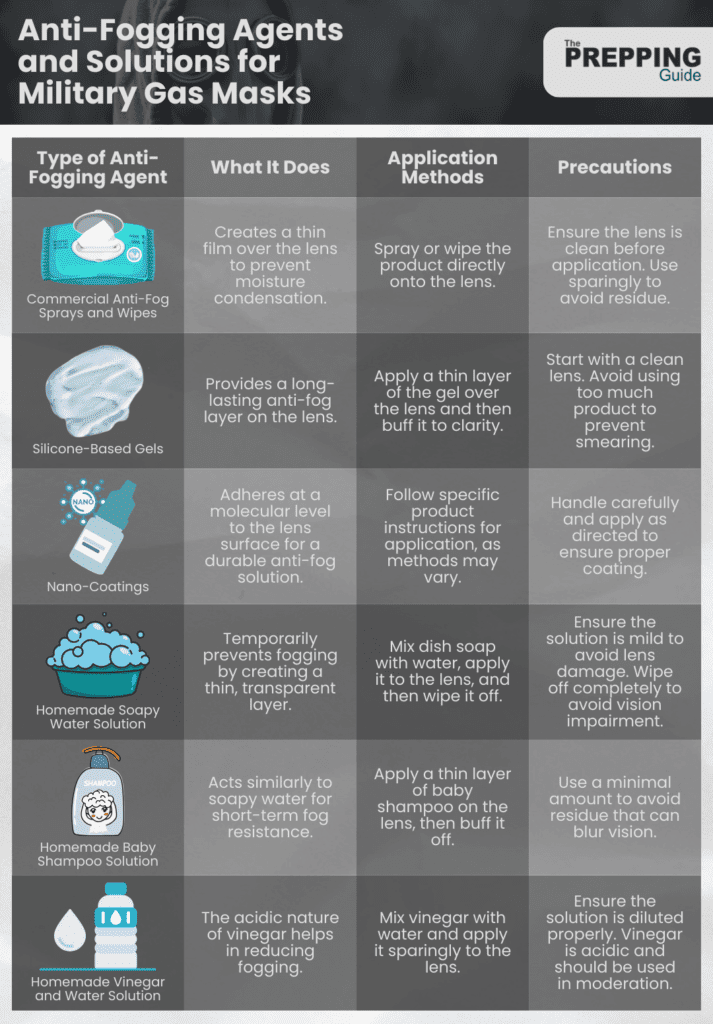
We’ll explore the best options available and how to apply them safely and effectively.
Best Commercial Anti-Fog Products for Military Masks
For those looking for reliable and tested solutions, several commercial anti-fog products stand out for their effectiveness with military gas masks. These products have been formulated to provide clear vision even under challenging conditions.
- Anti-Fog Sprays and Wipes: Brands like FogTech® DX and Sven Can See® offer sprays and wipes specifically designed for use on gas mask lenses. These products create a thin film over the lens that prevents moisture from condensing.
- Silicone-Based Gels: Products such as Cat Crap or Quick Spit Anti-Fog Gel are popular for their long-lasting effect. They can be applied thinly over the lens and buffed to clarity, providing a durable anti-fog layer.
- Nano-Coatings: Some newer technologies involve nano-coatings that adhere at a molecular level to the lens surface, offering a long-term solution to fogging issues.
Homemade Anti-Fog Solutions for Quick Fixes
For those who prefer a DIY approach or find themselves in a situation without access to commercial products, homemade anti-fog solutions can be quite effective. These can be easily prepared with common household items.
- Soapy Water Solution: A simple mixture of dish soap and water applied to the lens and then wiped off can prevent fogging temporarily.
- Baby Shampoo: Similar to the soapy water solution, a thin layer of baby shampoo applied and then buffed off can provide short-term fog resistance.
- Vinegar and Water Solution: A mixture of vinegar and water can also be effective. The acidic nature of vinegar helps in reducing fogging when applied sparingly.
Safe Application Techniques for Anti-Fog Agents
Applying anti-fog agents safely and effectively is crucial to ensure they perform as intended without damaging the mask.
- Clean the Lens First: Always start with a clean lens. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to remove any dirt or debris.
- Apply Sparingly: Whether it’s a commercial product or a homemade solution, apply it sparingly. A thin, even layer is usually sufficient.
- Buff to Clarity: After application, gently buff the lens with a soft cloth until it is clear. This helps in spreading the solution evenly and ensures no residue is left behind.
3. Doing Ventilation and Breathing Techniques
The ventilation system of a gas mask is a critical component in preventing lens fogging. This system is designed to facilitate the flow of air, allowing exhaled air to exit the mask while bringing in fresh air. Ensuring that the ventilation system is functioning optimally involves regular checks and maintenance.
Clearing any blockages in the exhaust valves and ensuring that they are in good working condition are essential steps. Additionally, the intake valves should be inspected to make sure they are providing adequate airflow without allowing contaminants in.
In some advanced masks, the ventilation system can be adjusted to suit different environmental conditions. Adjusting these settings can help in controlling the internal temperature and humidity levels within the mask, which in turn reduces the likelihood of fogging. For example, in colder environments, reducing the influx of cold air can help maintain a more consistent internal temperature, minimizing condensation on the lens.
Effective Breathing Techniques to Reduce Fogging
Mastering certain breathing techniques can also be a powerful tool in reducing fogging inside a gas mask. These techniques help manage the moisture and temperature of the air inside the mask, which are key factors in fogging.
Controlled Breathing

This technique involves taking slow, deliberate breaths. The idea is to reduce the overall humidity and temperature within the mask, which are elevated by rapid, deep breathing.
When you breathe slowly and with control, you decrease the volume of warm, moist air that reaches the cool lens of the mask, thus reducing the chance of fogging. This method requires some practice but can be highly effective. Controlled breathing is especially useful during periods of low physical exertion, where the need for oxygen is reduced.
Shallow Breathing
When engaged in more strenuous activities, or if fogging begins to occur despite controlled breathing, shallow breathing can be an alternative strategy. This involves taking more frequent but less deep breaths.
By reducing the depth of each breath, the amount of warm air reaching the mask’s lens is minimized, helping to prevent fog buildup. This technique can be particularly useful in situations where adjusting the mask or using other anti-fogging methods is not feasible.
Breath Direction
The direction of your breath can also impact the likelihood of fogging. When you exhale, directing your breath downwards or away from the lens can help prevent warm air from condensing on the cooler lens surface.
This can be achieved by positioning your tongue towards the roof of your mouth and exhaling downward, or by slightly angling your jaw downwards. This method may require some practice to become effective but can be combined with controlled or shallow breathing techniques for better results.
4. Maintaining a Dry Environment
Maintaining a dry environment inside the gas mask is key to preventing fogging. This involves selecting the right clothing, minimizing sweating, and understanding how to effectively use a gas mask in challenging weather conditions like high humidity and rain.
Choosing the Right Moisture-Control Clothing
The selection of appropriate moisture-control clothing is a vital aspect of managing internal humidity when wearing a gas mask. The right clothing can significantly reduce the amount of moisture that accumulates inside the mask, thereby lowering the risk of fogging.
Moisture-Wicking Fabrics
Moisture-wicking fabrics are specifically designed to pull sweat away from the skin and transport it to the outer surface of the garment, where it can evaporate more easily. This technology keeps the skin drier and cooler, which is particularly beneficial in the facial area under a gas mask.
Fabrics like polyester, nylon, or specialized blends are commonly used for their moisture-wicking properties. When choosing undergarments, headwear, or balaclavas to wear under a gas mask, it’s advisable to opt for these materials.
Breathable Layers
In addition to moisture-wicking fabrics, wearing breathable layers is key to managing heat and moisture. Breathable materials allow air to circulate close to the skin, aiding in the evaporation of sweat and the regulation of body temperature.
This is particularly important in the layers closest to the skin. Garments with ventilation features, such as mesh panels or breathable membranes, can be particularly effective.
Water-Resistant Outerwear
In wet or humid conditions, water-resistant or waterproof outerwear is essential to prevent external moisture from affecting the wearer. Such outerwear should be capable of repelling water while still allowing for some level of breathability to prevent excessive internal condensation.
Materials like Gore-Tex or other waterproof breathable fabrics are ideal choices. Additionally, ensuring that the outerwear fits well with the gas mask and doesn’t force moisture up into the mask area is crucial.
Tips to Minimize Sweating While Wearing a Gas Mask
Reducing sweating is an important factor in maintaining comfort and visibility when wearing a gas mask. Here are some tips to help manage sweating:
Hydration

Staying well-hydrated is crucial for effective body temperature regulation. Adequate hydration helps the body to cool itself more efficiently, reducing the tendency to sweat excessively. Drinking water regularly, even when not feeling thirsty, is important, especially in hot or strenuous conditions.
Pace Yourself
It’s important to manage physical exertion, especially in warm or humid environments. Overexertion can lead to increased sweating, which in turn can lead to more moisture inside the mask. Taking regular breaks and pacing physical activities can help to keep body temperature and sweating under control.
Adapt to Environment
Before donning the gas mask, spend some time in the environment to allow your body to acclimatize to the ambient temperature. This acclimatization can help reduce the shock of temperature change when putting on the mask, which can often lead to immediate sweating. This is especially important in extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold.
5. Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning of a military gas mask is a vital process that ensures its effectiveness and longevity. This routine should be performed after each use or at regular intervals during periods of sustained use.
- Disassemble: Begin by carefully disassembling the mask according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually involves detaching the filters, removing any external attachments, and separating the facepiece from other components. It’s important to handle each part delicately to avoid any damage and to note the correct assembly for reassembling later.
- Cleanse: Once disassembled, each component should be cleaned thoroughly. For the facepiece and non-electronic parts, use a mild, non-abrasive cleaner. You can use a soft brush or cloth to gently clean the surfaces. For sensitive parts and filters, follow specific cleaning instructions provided by the manufacturer. Avoid using harsh chemicals, solvents, or abrasive cleaners, as these can damage the materials of the mask and reduce its protective capabilities.
- Dry: After cleaning, each part should be air-dried completely in a well-ventilated area. Avoid direct sunlight or heat sources, as these can warp or degrade the materials. Ensure that no moisture remains, especially in crevices and around seals, as this can lead to mold growth or material deterioration.
Inspect and Replace: Keeping Your Mask Battle-Ready

To ensure a gas mask remains reliable and functional, regular inspection and timely replacement of parts are essential.
- Inspect Seals and Valves: Examine the seals and valves closely for any signs of wear, cracks, or damage. These components are crucial for maintaining an airtight seal and proper airflow. Any degradation can compromise the mask’s protective capabilities.
- Check for Cracks or Breaks: Carefully inspect the body of the mask and its straps. Look for any signs of cracks, breaks, or material fatigue. Pay special attention to areas that are subject to frequent stress or bending. Even small cracks can greatly diminish the effectiveness of the mask in a hazardous environment.
- Timely Replacement: If any parts are found to be damaged or excessively worn, they should be replaced immediately. Always use parts that are specifically designed for your model of gas mask, as using incompatible components can lead to failure of the mask. Keeping a stock of essential spare parts can be helpful for quick replacements.
Additional Tips and Accessories
Beyond the basic maintenance and usage techniques, there are additional accessories and tips that can further enhance the functionality of a gas mask. These add-ons are designed to improve comfort, visibility, and overall performance, especially in challenging conditions.
Let’s explore how anti-fog inserts, microfans, and compatibility with night vision devices can significantly enhance the efficiency of gas masks.
Using Anti-Fog Inserts and Films
One effective way to combat lens fogging is through the use of anti-fog inserts and films. These are specially designed to fit inside the gas mask lens, creating a barrier that prevents the buildup of condensation. Anti-fog inserts are typically made from moisture-absorbing materials that trap moisture before it can fog the lens, maintaining clear vision. They are often easy to install and can be replaced as needed.
In addition to inserts, anti-fog films can be applied directly to the lens of the gas mask. These films are usually thin and transparent, treated with anti-fogging chemicals that minimize the surface tension of water droplets, causing them to spread out thinly rather than form fog. This technology ensures that even in situations of rapid temperature changes or high humidity, the mask’s lenses remain clear, thereby not obstructing the wearer’s vision.
Adding Microfans

Integrating microfans into gas masks is an innovative approach to maintaining clear vision and comfort. These small, battery-operated fans are designed to fit within the mask and create a continuous flow of air.
This airflow helps to circulate the air inside the mask, reducing the buildup of heat and moisture, key factors that contribute to fogging. Microfans can be particularly beneficial in strenuous activities or in environments where the air is stagnant and humid.
The use of microfans also contributes to overall comfort. By reducing the temperature and moisture within the mask, they make it easier for the wearer to breathe and reduce the claustrophobic feeling that can come with mask-wearing.
The fans are typically designed to be lightweight and quiet, ensuring they do not interfere with the wearer’s activities or communication.
Ensuring Night Vision Device Compatibility with Gas Masks
For military operations that extend into low-light conditions, compatibility with night vision devices (NVDs) is essential. Gas masks need to be designed or adjusted in a way that allows the wearer to use NVDs effectively. This involves ensuring that the mask does not obstruct the field of view or interfere with the positioning of the devices.
Design considerations include the shape and size of the mask, particularly around the eye area. Some masks come with specific attachments or have adjustable straps to allow for a better fit with NVDs. It’s also important to consider the lens material and coating of the mask, as these should not distort or reduce the effectiveness of the night vision technology. Adapting gas masks for NVD compatibility enhances the operational capabilities of military personnel, allowing them to perform effectively in a range of lighting conditions.
Quick Fog Clearing Strategies
In dynamic field situations, where every second counts, having quick strategies to clear fog from gas mask lenses can be crucial for maintaining visibility and operational effectiveness. These strategies are designed to provide immediate solutions to fogging issues, ensuring that military personnel can quickly regain clear vision without compromising their safety or the integrity of their protective gear.
Temporary Mask Adjustment
This technique involves making a brief, slight adjustment to the mask to allow a small amount of outside air to enter. This can be done by gently pulling the mask away from the face for a moment, allowing warmer, moist air inside the mask to be replaced by cooler outside air. This exchange can help to quickly clear fogged lenses.
It’s important to ensure that this is done in an environment where it’s safe to momentarily break the seal of the mask, as this could expose the wearer to contaminants. The key is to make the adjustment quick and minimal, just enough to defog the lens without significantly compromising protection.
Using Absorbent Materials

Using small, absorbent materials inside the mask is a preventative measure that can help manage moisture buildup, one of the primary causes of fogging. Materials such as anti-fog cloths, small sponges, or even pieces of clean cotton fabric can be strategically placed near the nose and mouth area. These materials absorb moisture from the breath, reducing the amount that reaches the lens. It’s crucial to ensure that these materials are placed in a way that they do not obstruct breathing or interfere with the mask’s seal and functionality. Regular replacement or drying of these materials is necessary to maintain their effectiveness.
Manual Wiping
In situations where it’s safe to do so, quickly removing the mask to manually wipe the lens with a clean, soft cloth can provide immediate defogging. This method is straightforward but should be used cautiously, as it involves exposing the face to the external environment. It’s best reserved for situations where other methods are not feasible, and the environment is confirmed to be free of immediate threats. When wiping the lens, use a gentle, circular motion to avoid scratching or damaging it. This method is also useful as a last resort if fogging occurs during a break in operations or in a controlled environment.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, managing fogging in military gas masks requires a multifaceted approach that includes proper fit, regular maintenance, and the use of specialized accessories and techniques. Understanding and adapting to environmental conditions, along with integrating innovative solutions like anti-fog inserts, microfans, and ensuring compatibility with night vision devices, enhances the functionality and reliability of gas masks.
By employing these strategies and being prepared for real-world scenarios, military personnel can ensure their gas masks provide maximum protection and clarity, essential for operational effectiveness and safety.
