Data is becoming an increasingly valued asset in the current digital era. It is crucial for preppers, especially, to have a reliable data backup plan to guarantee that your vital information is safe in case of an emergency or tragedy. But how often should you do a data backup? Is there a general principle or best practice to adhere to?
You should manually or automatically back up your essential data at least weekly, ideally once every 24 hours. Generally, the requirement to frequently back up your data increases with its value and significance.
Continue reading to learn how often you should back up your data and the best backup strategies you can follow.
Quick Navigation
- Why is Data Backup Important?
- Where Should You Keep Your Data Backups?
- How About Data Center Backup Solutions?
- How Often Should You Backup Data?
- Different Ways to Backup Your Data
- Best Practices for Backing Up Data
- Conclusion
Why is Data Backup Important?

Keeping good security and privacy is just as crucial as backing up your data when preventing adverse outcomes.
After all, you can always revert to your most recent backup if a system is lost, hardware malfunctions, or, God forbid, someone hacked you.
Most business data comprises financial, customer data, and corporate data, depending on the market your organization serves.
If all this data is kept on a single, personal computer, losing it would make replacing it difficult and expensive.
Backing up data is copying files to restore them in the case of data loss. Data loss may result in several circumstances, including theft, hardware failures, file corruption, and natural disasters such as floods and fires.
It is critical to have your data backed up and have a disaster recovery policy always in place.
In the case of a primary data failure, the backup’s goal is to duplicate the retrievable data. Primary data failures may come from data corruption, hardware or software issues, or human errors.
Where Should You Keep Your Data Backups?
Depending on your needs and requirements, there are different data storage for backing up data.
Online/Cloud
Whatever happens to your network or physical location, your data is protected if you store it in the cloud or another virtual location.

Cloud storage alternatives are plenty. Cloud backups may be automated, making their management more straightforward.
You can securely back up data to the cloud and store it remotely to keep it safe off-site. If anything occurs to your physical company or hardware and you can no longer access your data locally on your computers, laptops, gadgets, or hard drives, this configuration is crucial.
Local/On-Site
Local or on-site backup is practical because you always have access to what you need when you need it, whether on your server or on smaller devices like USB jump drive.

Local or on-site backup, however, won’t shield your whole network, mainly if a disaster like a fire or a flood brings on the loss.
Off-Site
On external hard disks maintained off-site, you may store data off-site similarly to local backup. You can print critical files as well.

Although printing still runs the danger of misplacement or ending up in the wrong hands. It also makes it harder for you to retrieve the backup when you need it most.
How About Data Center Backup Solutions?
Data Center Backup Software can prevent human mistakes and provide a seamless backup procedure for corporate data. These provide many practical advantages while reducing the hazards of a single, physical storage place.

Data Center Backups are crucial because a typical data center offers various data-related services, sometimes under contract to its customers and frequently for mission-critical use.
Data center backup is a much more complex process than many people realize. It involves creating actual backups of different nodes and systems inside of the data center but also setting up and maintaining a thorough backup infrastructure.
This system also includes creating backup copies of components like cooling resources, data center power, etc.
Users have many alternatives for Data Center Backup Software like Rubrik, Veeam, Veritas, and Commvault Complete Data Protection.
Users will get features like an automatic backup they may schedule as needed, although not all providers offer this feature.
How Often Should You Backup Data?
Computer crashes are common and may often lead to damaged equipment and lost data. Regular backups are the only effective backup strategy to safeguard your company’s valuable digital assets.
When choosing a backup frequency, you should consider the following concerns, according to Microsoft:
- How crucial are the data stored on your systems?
- What type of information is in the data?
- How often are the statistics updated?
- How fast must the data be recovered?
- Do you own the tools necessary to conduct backups?
- Who will be in charge of creating the backup and complete recovery strategy?
- What time of day or week is ideal for scheduling backups?
- Do you need off-site backup storage?
According to many data center backup professionals, the most important of these queries is how often your data changes. Today, most businesses are engaged in producing fresh content.
Blog posts, emails, consumer data, policy papers, and more are all examples of the new data produced daily—almost every minute. Organizations must continue to back up all of this additional data in light of this.
An IT professional would tell you that frequent backups are something you should do. You should back up important data at least once per day. You may save important files to external hard drives, cloud storage, or other external sites to ensure data preservation if one or more on-site computers are damaged.
By ensuring that data is automatically uploaded and stored whether or not someone remembers to do the backup, scheduling backups to occur automatically is an excellent technique to prevent losing valuable data.
Keep any external hard drives in a safe place, such as a locked, fireproof safe or an off-site storage facility. This safekeeping will guarantee that the data will remain secure even if a fire or other calamity damages your facility.
Different Ways to Backup Your Data
Various backup options are available based on your unique requirements.
Complete or Full Backup
Full data backup essentially means backing up everything. You may fully restore your company’s assets in the most current, single backup version with a complete data backup.
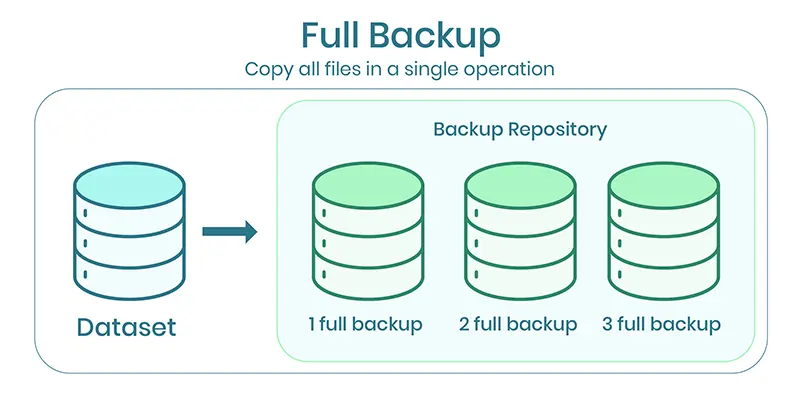
This type of backup requires plenty of time, bandwidth, and storage space.
Differential Backup
A differential backup ignores incremental backups and includes changes made since the previous complete backup.
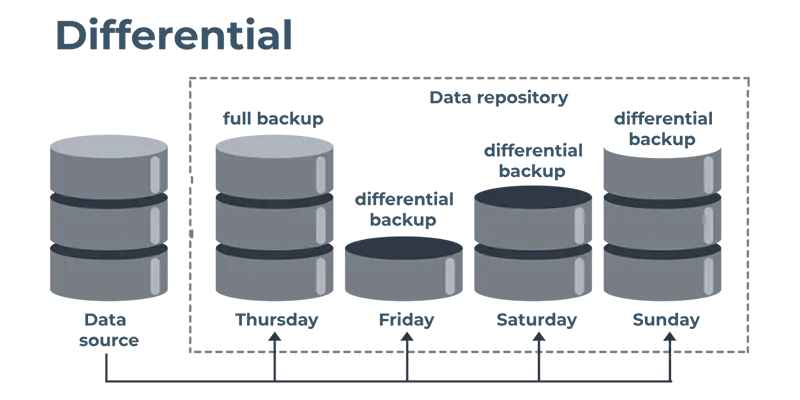
The differential backup takes and updates everything modified since the full backup on Friday, for instance, if you finish a full backup on Friday, an incremental backup on Monday, and a differential backup on Tuesday.
Incremental Backup
An incremental backup uses the least space, bandwidth, and time compared to a complete backup. This procedure creates copies of the files while considering any modifications since the previous complete or incremental backup.
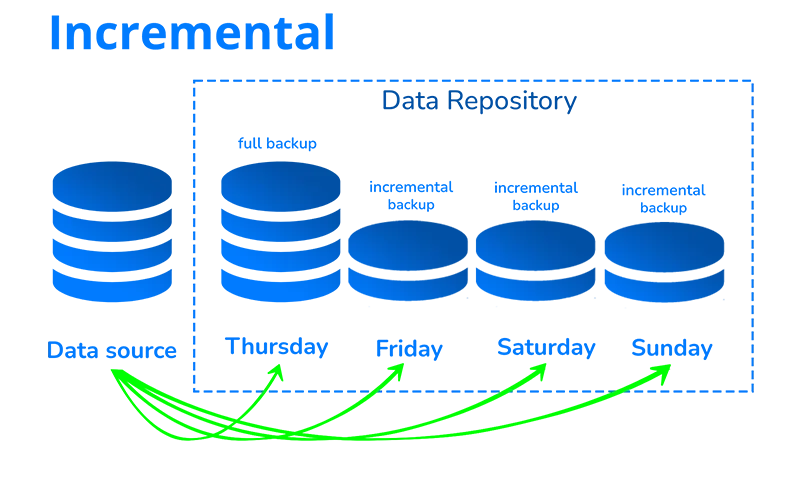
Let’s imagine, for illustration, that your company has finished a full backup. Then you do an incremental backup after creating a few more files.
Because the files in the complete backup are identical, this incremental backup detects only the copies of the two new files. As fewer files need backing up, this saves time and storage space.
Continuous Backup
The continuous approach is backing up data every time there are changes made. It generates an electronic journal of snapshots when a data update takes place.
Additionally, restoring the most recent clean copy of the damaged file is always possible if the system has computer viruses or a corrupted file has been unnoticed for a while.
Best Practices for Backing Up Data
There are some backup practices and strategies that you can follow to ensure total data security.

3-2-1 Backup Rule
Making sure that your data is dependably recoverable can be done using a 3-2-1 backup approach. This process involves making copies – you make three copies of your data, at least two on various media and one kept off-site.
Regular Backup Testing
The main goal of backup testing is to ensure the company can recover its data and continue with business as usual.
In addition to the data security strategy, backup policies should be in the context of more significant business continuity or disaster recovery plans.
Encryption and Security
Backups are increasingly becoming a top target for hackers because they seek to eliminate your capacity to take control of your data.
Backup encryption is thus crucial for improving your overall security posture, business continuity, and catastrophe recovery.
Backup encryptions are security practices that protect contact information and sensitive data for your personal or company and deter illegal access.
Take note that if you will be doing the entire process using public connections, it’s a good idea to use a VPN. Although it’s not entirely necessary, it can be helpful in keeping your data secure.
Conclusion
More than half of all company data losses are due to hardware issues and software errors. Using the proper data backup strategy, small businesses may prevent subsequent, far more expensive losses.
You may ensure that your important data is secure and accessible in catastrophes, natural disasters, or any other unanticipated events by taking a proactive approach to performing backups.
Data backup is a crucial step in being ready for anything, and it’s essential to remember that prevention is always preferable to cure. Instead of being compelled to take remedial action after a data loss, it helps you to be proactive with your data management.
